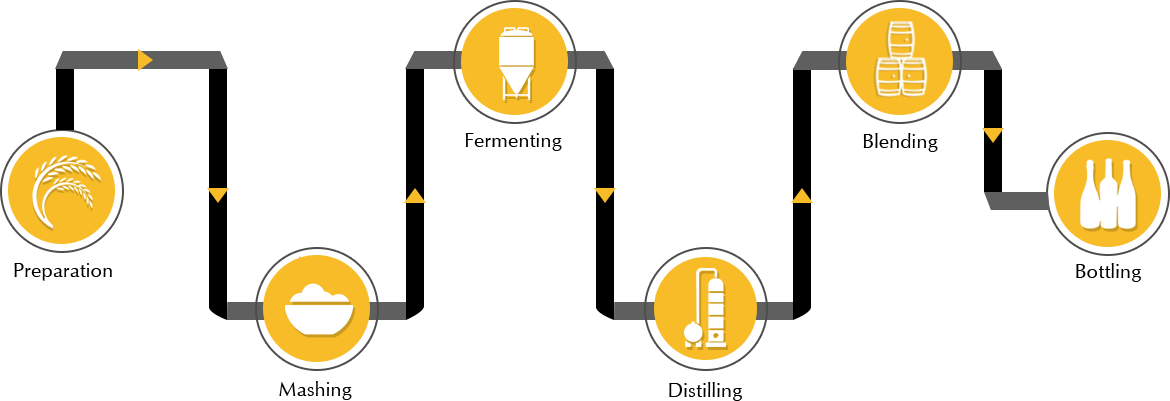
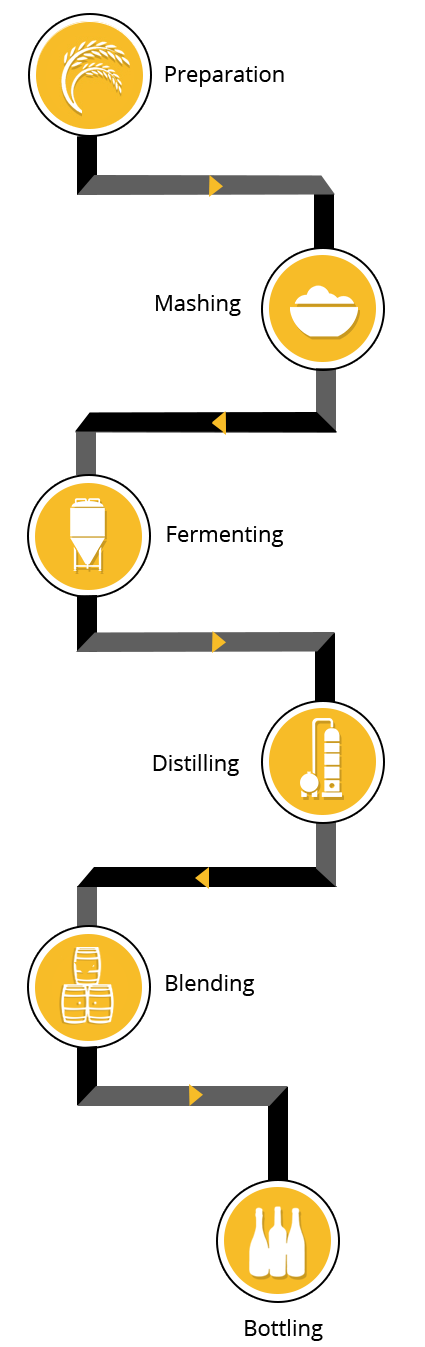
Mashing involves operations such as slurry preparation, jet cooking, and enzymatic hydrolysis. ‘Slurry Preparation’ – Weighted flour is mixed with hot water to produce a slurry with 20-30% dissolved solids and mixture is made in a tub where the starch granules swell and gradually rupture known as gelatinization of starch.
‘Jet Cooking’ – This is done by mixing the slurry with live steam (online) in a static mixer. ‘Enzymatic hydrolysis’ - The cooked slurry is then flashed to atmospheric pressure in a flash vessel. Here enzymes are rapidly hydrolyzed and gelatinize starch into smaller and soluble fragments called dextrins. These fragments are further converted into simple fermentable sugar with the help of an enzyme.